How Co-Teaching Transforms SEN Classrooms Worldwide
16th September 2025

Inclusive classrooms thrive when teachers collaborate. Around the world, co-teaching models have emerged as powerful strategies to support students with Special Educational Needs (SEN). By combining the expertise of general and special education teachers, co-teaching ensures that every student has access to personalized support without being isolated from peers.
For educators looking to adopt these practices, enrolling in Special Educational Needs Online Courses or Online Special Education Courses can provide the skills and strategies to implement co-teaching effectively, making classrooms more inclusive and supportive for all learners.
In this blog, we’ll explore proven co-teaching models from around the globe and how they can be adapted for SEN classrooms.
Popular Co-Teaching Models Used Worldwide
Co-teaching can take many forms, each offering unique benefits for SEN classrooms. Below are some of the most widely used models around the world and how they help teachers create inclusive, effective learning environments.
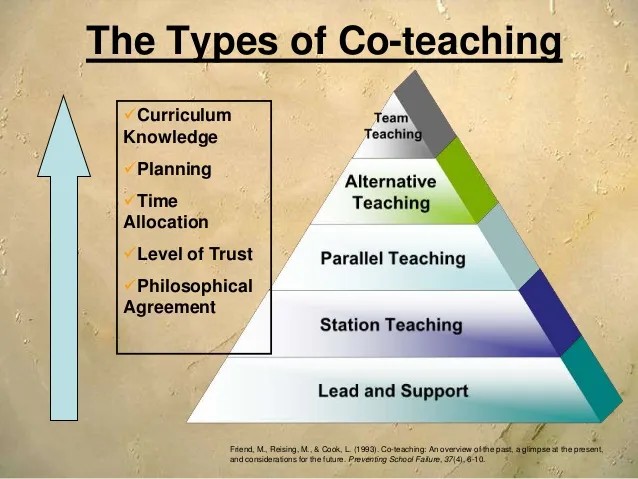
1. One Teaching, One Observing
In this model, one teacher delivers the lesson while the other observes students’ learning behaviors, participation, and progress. The observing teacher collects valuable data that can be used to refine instruction and provide targeted support for SEN learners. This is particularly effective for identifying subtle learning challenges that may otherwise go unnoticed.
2. One Teaching, One Assisting
Here, one teacher leads the instruction while the other moves around the classroom, providing immediate help to students who need clarification or extra guidance. This ensures SEN students receive ongoing support without interrupting the flow of the lesson. Common in US and UK classrooms, it keeps students engaged while addressing individual needs.
3. Station Teaching
Teachers divide the class into groups that rotate between stations, each focusing on different activities. One station may emphasize core instruction, while another targets skill development or SEN-specific support. This is widely practiced in European schools to facilitate differentiated learning.
4. Parallel Teaching
The class is split into two groups, with each teacher teaching the same content simultaneously. Smaller groups give SEN students more opportunities to interact, ask questions, and receive personalized attention.
5. Team Teaching
Both teachers actively share the instruction, taking turns or co-delivering lessons in a conversational style. This approach, common in Finland and Australia, provides multiple perspectives and teaching styles, enhancing inclusivity.
6. Alternative Teaching
One teacher works with a smaller group of students, often SEN learners, while the other manages the larger group. This allows for specialized instruction without completely isolating SEN students from their peers.
Global Insights: What Works Best
- United States: Many schools use One Teaching, One Assisting to provide real-time classroom support, as well as One Teaching, One Observing to track SEN student progress and adjust strategies accordingly.
- Finland: Known globally for inclusive education, Finnish schools often rely on team teaching, ensuring that no student is marginalized and that SEN learners thrive in mainstream classrooms.
- Japan: Station teaching and strong collaborative planning between teachers are emphasized, striking a balance between mainstream learning and individualized SEN support.
- Australia: Parallel teaching and alternative teaching are common, especially in rural areas where SEN resources are stretched and flexible classroom models are necessary.
- India: With increasing attention to inclusive education, schools are experimenting with station teaching and alternative teaching models, supported by training from Online Special Education Courses.
- Singapore: Co-teaching is integrated into national inclusive education frameworks, with team teaching and one-assistant models widely applied in SEN-support classrooms.
- United Arab Emirates (UAE): Schools emphasize alternative teaching and parallel teaching to ensure SEN students receive dedicated support in rapidly diversifying classrooms.
These examples show that co-teaching is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Instead, schools adapt models based on class size, student needs, teacher expertise, and cultural context—making flexibility and training key to success.
How SEN Teachers Can Prepare for Co-Teaching
Adopting co-teaching requires:
- Strong collaboration and communication between teachers.
- Training in inclusive strategies and differentiated instruction.
- Flexibility to adapt teaching methods based on student needs.
This is where professional development plays a vital role. Courses like Special Educational Needs Online Courses or Online Special Education Courses prepare teachers to apply global co-teaching strategies effectively in their own classrooms.
Conclusion
Co-teaching is more than just sharing a classroom—it’s about creating inclusive, student-centered learning environments where SEN learners can thrive. From station teaching to team teaching, these models demonstrate how collaboration transforms classrooms into spaces of equal opportunity.
For educators eager to adopt these strategies, structured learning through Online Special Education Courses, provides the tools and insights needed to adapt co-teaching models successfully. With the right training and mindset, SEN teachers can make inclusive education a reality for every student, everywhere.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is co-teaching in SEN education?
Co-teaching is when two educators, usually a general education teacher and a special education teacher, work together in the same classroom. They share responsibility for planning, teaching, and supporting students, ensuring SEN learners get equal access to education.
2. Why is co-teaching important for SEN classrooms?
It promotes inclusion, reduces barriers, and provides individualized support without separating SEN learners from their peers. Co-teaching helps SEN students thrive academically and socially.
3. What are the most effective co-teaching models?
Popular models include One Teaching, One Observing, One Teaching, One Assisting, Station Teaching, Parallel Teaching, Team Teaching, and Alternative Teaching. Each has unique strengths depending on student needs and class size.
4. Which countries use co-teaching models successfully?
Countries like the US, Finland, Japan, Australia, India, and Singapore have adopted different co-teaching strategies, tailoring them to cultural and classroom contexts.
5. How can teachers prepare for co-teaching?
Professional training is key. Programs such as Online Special Education Courses help teachers develop the skills to collaborate effectively and adapt co-teaching models for SEN classrooms.
Written By : Park Jin Ae

